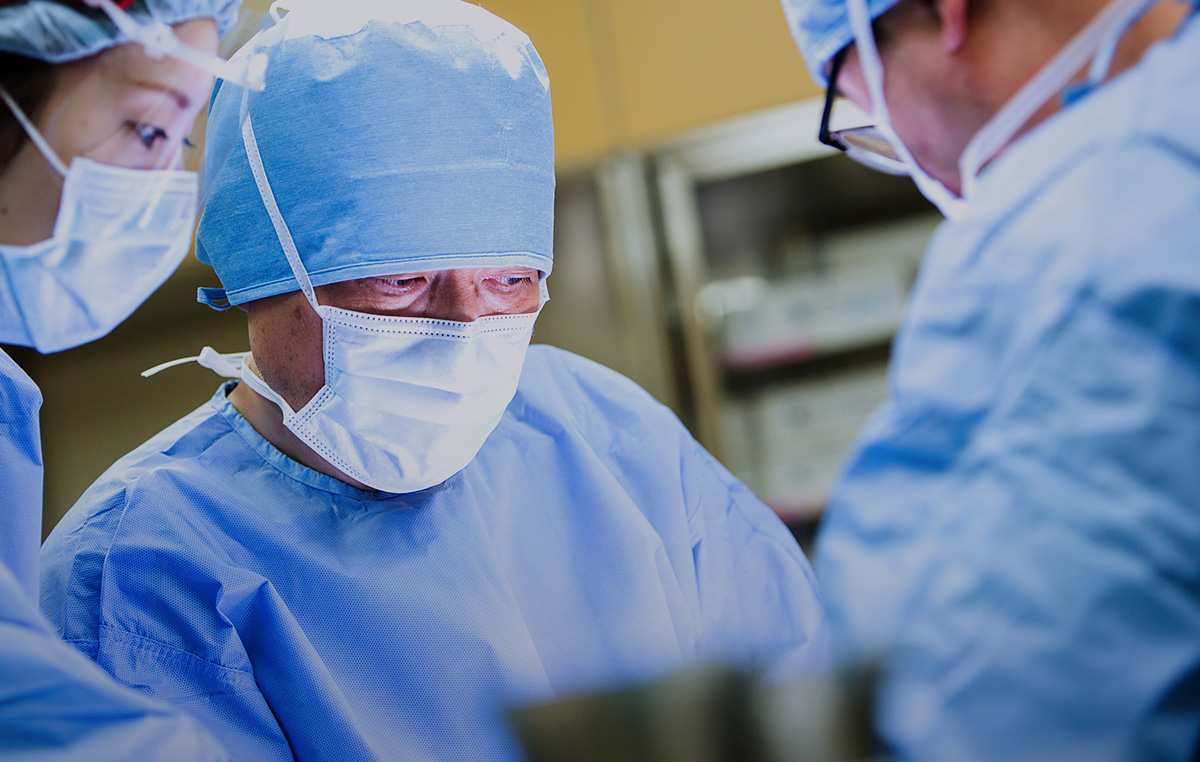
At NTT Medical Center Tokyo, we’re committed to providing personalized medical care rooted in our community.
As a regional core medical center, we work closely with our local community,
fostering collaboration among our staff to deliver comprehensive and compassionate care.
With our expertise in areas such as early cancer detection, minimally-invasive procedures,
and emergency treatment, we strive to build strong connections with our patients.
We aim to extend our reach and connect with individuals worldwide.


In 2016, NTT Medical Center Tokyo was selected as one of only 69 international patient-friendly hospitals in Japan.
In 2021, we opened the Department of International Healthcare, now staffed with multiple doctors with ample overseas training and experience.
Our international patient services division is staffed with 7 English interpreters, 1 Chinese interpreter, and 1 Italian interpreter that are able to assist you from start to end of your consultation(as of July 2024).
Cancer treatment is constantly evolving.
NTT Medical Center Tokyo focuses on early detection and minimally invasive procedures.
We also provide comprehensive rehabilitation services to help our patients return to their normal daily activities after treatment.

NTT Medical Center Tokyo employs various minimally invasive treatment methods for tumor removal.
Examples:
- Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD)
- This procedure utilizes an endoscope to remove early-stage stomach and intestinal cancer without the need for a laparotomy (open surgery).
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- Applied for liver cancer and other conditions, this technique inserts an electrode into the lesion to destroy the cancer through thermocoagulation by electromagnetic waves, eliminating the need for a laparotomy (open surgery)
- Robotic Surgical Assistance (da Vinci)
- Commonly used for prostate cancer, this method promises reduced bleeding, postoperative pain, and fewer complications compared to traditional laparotomy.
- Robotic Arm Assisted Surgery (Mako System)
- The Mako system is an innovative tool for orthopedic surgeries such as hip replacements and knee replacements. It is typically used to treat osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joints. This technology allows surgeons to achieve greater accuracy in surgery.
- Gamma Knife Treatment
- This radiotherapy is used for brain tumors and other conditions. It destroys cancer by focusing radiation (gamma rays) on the lesion, controlled by a computer, without the need for a craniotomy (open surgery)
In 2003, our hospital was designated as a regional cancer hospital by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. This designation is renewed every four years, with the most recent renewal in April 2023. The current designation as an advanced regional cancer hospital is valid from April 1, 2023, to March 31, 2026.

NTT Medical Center Tokyo excels in early cancer detection through a multidisciplinary approach. Our specialists employ advanced techniques to ensure accurate measurements and interpret ultrasound, CT scans, and tissue samples effectively.



At NTT Medical Center Tokyo, we specialize in endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for early gastrointestinal cancer, including cancer of the esophagus, stomach, duodenum, and large intestine. ESD offers a minimally invasive alternative to laparotomy, reducing post-treatment complications and patient discomfort. Due to its benefits, there’s a growing demand for ESD among patients, with an increasing number of doctors seeking training in this technology. We performed 1042 ESD cases from January to December 2023. As of July 2024, we have a team of 17 doctors who are able to perform ESD. We’re also actively performing ESD for duodenum cancer, a cancer traditionally challenging to treat endoscopically. Our team is committed to optimizing ESD procedures to shorten treatment times, alleviating patient burden and thus enabling us to assist more patients.



NTT Medical Center Tokyo adopted the “da Vinci” surgical assistance robot in 2016. Primarily utilized for prostate cancer treatment, we conducted 121 procedures in 2023 alone. Robot-assisted surgery offers advantages such as decreased postoperative bleeding and pain, along with a lower risk of complications such as incontinence and erectile dysfunction. Our goal extends beyond cancer treatment; we strive to facilitate patients’ seamless return to their everyday lives post-treatment through da Vinci surgery.



Gamma knife treatment is a type of radiotherapy that targets brain tumors or vascular malformations with focused gamma rays, eliminating the need for a craniotomy. Conventional craniotomy surgery places a significant physical burden on the patient and is unable to treat certain areas. Gamma knife treatment is able to address these issues, making treatment possible. Metastatic brain tumors affect approximately 10% of cancer patients and significantly diminish the patient's quality of life by causing convulsions, paralysis, cognitive and emotional problems. While treating metastatic brain tumors may not lead to complete recovery, it is crucial for enhancing the patient's quality of life, allowing them to enjoy their remaining time as much as possible.


Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a liver cancer treatment that involves inserting an electrode into the abdomen and using high-frequency radio waves to heat and necrotize the lesion, avoiding the need for a laparotomy. NTT Medical Center Tokyo began utilizing RFA in 2006, and we performed in 229 cases in 2023. Even in situations where RFA is typically considered challenging, we may proceed with the treatment with patient consent and if the patient has no other options. We strive to improve patient prognosis day by day.

For acute conditions such as cerebral stroke or cardiac infarction,
it is well-established that a shorter interval between onset and treatment increases survival rates and reduces long-term complications.
NTT Medical Center Tokyo offers a 24-hour emergency support system to provide immediate care for these acute stage conditions.

NTT Medical Center Tokyo established its Stroke Unit in 2005 to provide emergency treatment for acute cerebral strokes.
We maintain a system that ensures available beds at all times for stroke patients requiring urgent care.
Our Stroke Unit is distinguished by three main features.
In April 2017, NTT Medical Center Tokyo established a cerebrovascular medicine division. This division collaborates with our neurosurgery department to offer 24-hour emergency treatment, including the administration of tPA in the acute stage of cerebral infarction and catheter-based cerebral embolism removal for severe cases.
We assemble multidisciplinary teams that include doctors from neurosurgery, cerebrovascular medicine, rehabilitation services, and radiation therapy, along with nurses, therapists, and social workers. These teams provide comprehensive support for patients, encompassing treatment, rehabilitation, and early reintegration into society.
Early rehabilitation for cerebral stroke in the acute stage is crucial for enabling patients to quickly reintegrate into society. At NTT Medical Center Tokyo, we have rehabilitation medicine specialists, who are separate from doctors that treat the stroke itself. Our team includes 26 physical therapists, 16 occupational therapists, and 8 speech therapists, who actively provide rehabilitation from the acute stage (as of July 2024).
Our cerebrovascular medicine and neurosurgery divisions cooperate
to select the most suitable treatment method for each patient.
- Surgical treatment
- ○Cerebral aneurysm clipping ○Cerebrovascular bypass surgery ○Carotid endarterectomy (CEA)
- Medical treatment
- ○Thrombolytic therapy with intravenous administration of tPA ○Cerebral embolism extirpation using a catheter
○Carotid artery stenting (CAS)
Acute stage treatment of cardiac infarction includes catheter-based stenting performed by the cardiology division and vascular bypass surgery conducted by the cardiovascular surgery division. Our cardiology and cardiovascular surgery teams collaborate closely to determine and provide the most appropriate treatment for each patient. We also emphasize cardiac rehabilitation following acute stage treatment. Our doctors and therapists in the rehabilitation service division work diligently to facilitate patients' early reintegration into society.

At NTT Medical Center Tokyo, 14 attending doctors are organized into three teams, which means that a patient is seen by multiple attending doctors. This structure enables us to provide high-quality treatment to all our patients while minimizing the risk of medical errors. The teams hold daily conferences to share detailed updates on their patients' conditions. In Japan, typically a patient is only seen by one attending doctor during admission.
Our system allows doctors to promptly respond to any events that may occur during patient admission or treatment. Our hospital boasts 5 certified and 2 instructing catheter treatment physicians of the Japanese Association of Cardiovascular Intervention and Therapeutics. (As of July 2024)
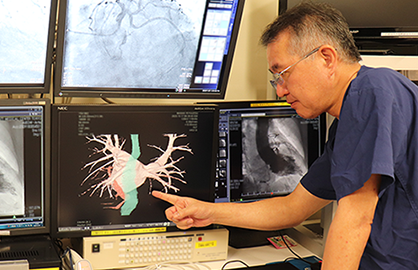
NTT Medical Center Tokyo has adopted OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography), a new vascular imaging diagnostic system using near-infrared radiation, to provide more detailed observations of diseased blood vessels, compared to the conventional IVUS (Intravascular Ultrasound). This advancement enhances the quality of acute stage treatment for cardiac infarction and allows for high-precision monitoring of the patient's condition after treatment.
Cardiac infarction is a serious condition that can be fatal if left untreated, but early intervention at a medical institution can significantly reduce the mortality rate. NTT Medical Center Tokyo has dedicated beds in its Coronary Care Unit (CCU) for treating cardiac infarction. Our CCU network is linked with neighboring medical institutions to ensure smooth patient admission and early initiation of treatment. (As of July 2024)
The management of acute-stage cerebral strokes is now predominantly medical. However, if this proves insufficient, transitioning to surgical intervention becomes imperative. Therefore, close collaboration between cerebrovascular medicine and neurosurgery divisions is paramount for effective stroke treatment.
At NTT Medical Center Tokyo, our neurosurgeons remain on standby to perform necessary surgical procedures. We also prioritize preventative measures against strokes, proactively performing cerebral aneurysm clippings on unruptured aneurysms using advanced microscopic techniques.
In 2023, our neurosurgery division successfully conducted 441 surgical procedures, including brain tumor surgeries. We consistently integrate our extensive experience into daily medical care, ensuring the highest standards of treatment for all our patients.



We provide emergency responses for cardiovascular diseases such as angina, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, valvular heart disease, and heart failure. Specifically, ischemic heart diseases like myocardial infarction often necessitate urgent intervention. Our hospital operates a 24-hour emergency support system for immediate catheter-based treatments. Additionally, we collaborate closely with our cardiovascular surgery division to promptly deliver emergency surgeries when needed.
We maintain daily updates on all patient statuses across our staff, enabling us to swiftly respond to unexpected situations, even in the absence of the attending physician. Furthermore, we are dedicated to enhancing regional medical care by establishing networks with local practitioners to ensure seamless post-discharge patient care.

NTT Medical Center Tokyo plays a crucial role in community-based medical treatment, focusing primarily on acute stage care. However, we recognize that comprehensive treatment cannot be achieved in isolation. We are committed to collaborating closely with local physicians to accept referrals for patients requiring surgery, hospitalization, or detailed examinations, ensuring smooth transitions back to their referring facilities after treatment.
Moreover, we are strengthening our connections with at-home care services and nursing, anticipating their growing importance in the future. Since implementing the registered doctor system in 2015, we have established partnerships with approximately 1,700 medical institutions, facilitating the sharing of information vital to our medical care (as of July 2024).
Additionally, we actively engage local doctors through clinical seminars and academic lectures, fostering cooperation to enhance the quality of medical treatment across the entire region.
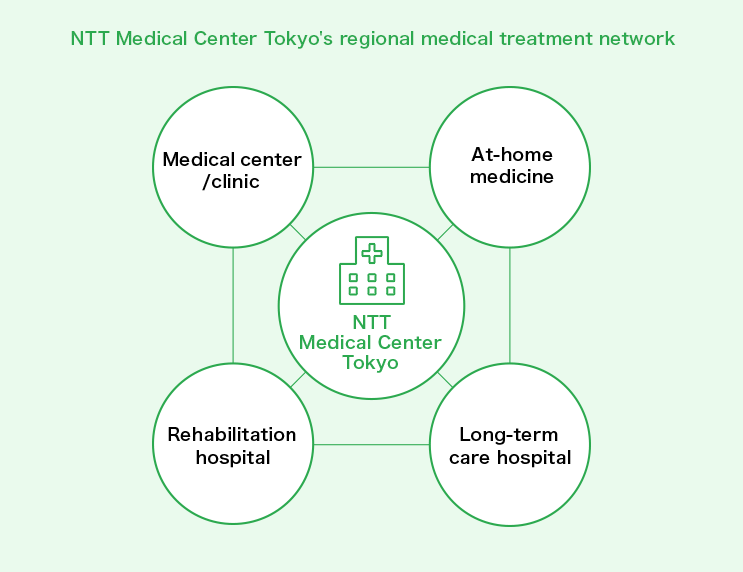
NTT Medical Center Tokyo was originally established as a hospital for employees of the Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation, and is still run by NTT East. We consistently prioritize contributing to community-based medical treatment over financial profit.
NTT Medical Center Tokyo is situated on the border of several wards, maintaining close connections with Shinagawa, Meguro, Shibuya, and Minato wards. Due to this strategic location, we have been designated as one of Tokyo’s 83 disaster base hospitals. This designation entrusts us with the primary responsibility of accommodating and treating critically injured patients in the event of large-scale disasters, such as earthquakes.
NTT Medical Center Tokyo has implemented a system allowing affiliated medical institutions to register with us. In line with the Japanese government’s “Coordination and Role-Sharing between Health Care Professionals” policy, we collaborate closely with doctors at other medical institutions, including local hospitals, to provide safe and high-quality medical care.
To ensure effective role-sharing between medical institutions, we request that all patients bring a letter of referral for their first visit.
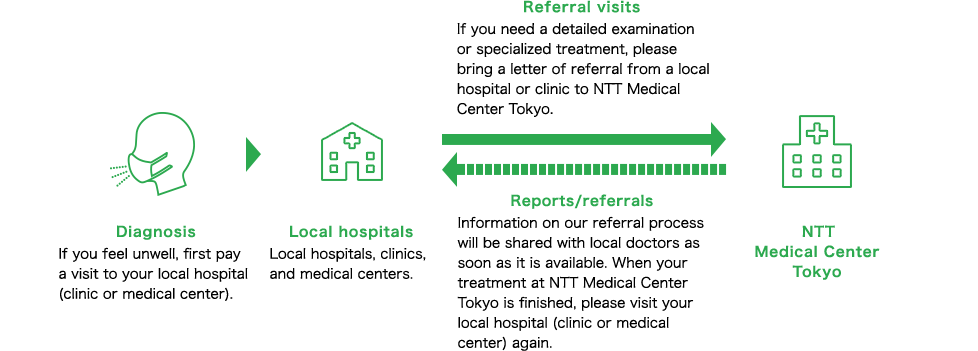
Please use the following formats if you are intending to make referral or use our high-cost hospital medical radiology imaging. For more details, please click on “Information For medical practitioners” and “Using hospital imaging”.
TEL: +81-(0)3-6721-6239 (main number)
5-9-22 Higashigotanda, Shinagawa-ku 141-8625
-

- Approximately 7 min. walk from Gotanda Station.
*We provide a shuttle bus from Gotanda Station.
-

- Approximately 5 min. walk from Gotanda Station.
-

- Usage fee: 100 yen/15 min.
Spaces available: 150
Open: 24 Hours